BasideWT- Whole Home Water Filtration System & Replacement
What is the Best Water Treatment System?
When it comes to ensuring clean and safe drinking water, one of the first questions that often arises is: What is the best water treatment system? With so many options available, selecting the most effective system can be overwhelming. Whether you’re concerned about water quality, contaminants, or taste, the right water treatment system can vastly improve your water.
This article delves into the various types of water treatment systems, the factors that influence their effectiveness, and how to choose the best option for your needs. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of the best water treatment solutions for your specific situation.
Why Do You Need a Water Treatment System?
Before we explore the various systems available, it’s important to understand why water treatment is so vital. Water sources, whether municipal or private wells, can contain harmful pollutants, minerals, and microorganisms that compromise health.
1. Microbial Contaminants
Contaminants like bacteria, viruses, and parasites are common in untreated water. Pathogens like E. coli and Giardia can cause severe illness, making it necessary to remove them through an effective treatment system.
2. Chemical Contaminants
In addition to microbes, chemical pollutants such as heavy metals, chlorine, and pesticides can also be present in water. These toxins pose long-term health risks, especially in high concentrations.
3. Aesthetic Improvements
Water treatment systems also improve the taste, odor, and clarity of water. Systems like activated carbon filters can reduce chlorine taste or remove foul smells caused by organic matter.
Types of Water Treatment Systems
There is no “one-size-fits-all” solution, as the best water treatment system depends on the type of contaminants, your water source, and your personal preferences. Below are some of the most popular and effective water treatment technologies available.
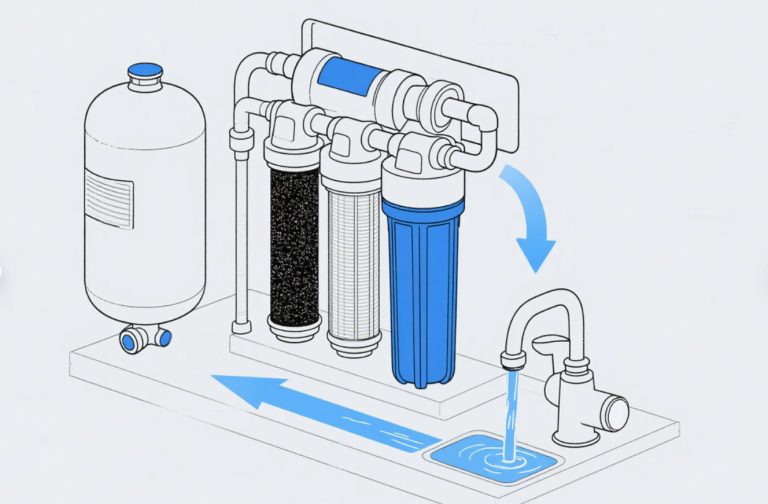
1. Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems
What is the best water treatment system? For many, reverse osmosis (RO) stands out due to its ability to filter out a wide range of contaminants, including bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, and salts.
- How it works: RO systems use a semi-permeable membrane to filter out contaminants. Water is forced through the membrane, leaving impurities behind.
- Pros: Removes a broad spectrum of contaminants, including dissolved solids and chemicals. It’s highly effective at purifying water for drinking and cooking.
- Cons: Requires regular maintenance, such as replacing membranes and pre-filters. It also wastes water in the filtration process, and some minerals are removed from the water.
2. Activated Carbon Filters
Activated carbon filters are one of the most common water filtration systems, primarily used to remove chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and bad odors.
- How it works: Activated carbon has a large surface area that adsorbs impurities as water flows through it.
- Pros: Effective at improving taste and odor, removes chlorine and VOCs, easy to install, and relatively low maintenance.
- Cons: Does not remove heavy metals or microorganisms. Needs to be replaced regularly to maintain effectiveness.
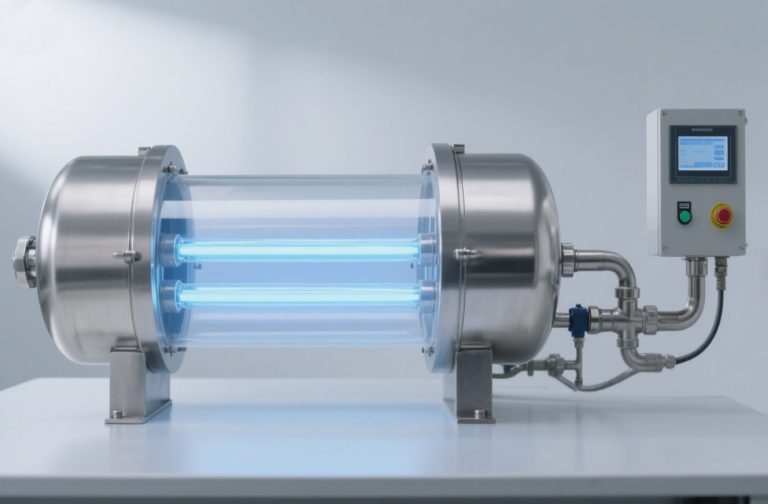
3. UV (Ultraviolet) Water Purifiers
UV water purifiers use ultraviolet light to disinfect water by destroying bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens.
- How it works: UV light disrupts the DNA of microorganisms, preventing them from reproducing and rendering them harmless.
- Pros: Very effective against bacteria and viruses, chemical-free, and low maintenance.
- Cons: Only disinfects water; does not remove chemical contaminants or particulate matter. The water must be clear for optimal performance.
4. Water Softeners
Water softeners are designed to remove minerals, particularly calcium and magnesium, which cause hardness in water.
- How it works: Softening systems typically use an ion exchange process, replacing calcium and magnesium ions with sodium or potassium ions.
- Pros: Prevents scale buildup in pipes and appliances, improves soap and detergent efficiency, and enhances the longevity of plumbing systems.
- Cons: Does not address other contaminants, such as bacteria or heavy metals. It also increases the sodium content in water.
5. Distillation Systems
Distillation is one of the oldest and most reliable methods of water purification. It involves boiling water and then condensing the steam back into liquid, leaving contaminants behind.
- How it works: Water is heated to its boiling point, and steam is captured and condensed into pure water.
- Pros: Removes nearly all contaminants, including bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, salts, and chemicals.
- Cons: Slow process, requires energy to boil water, and does not remove volatile compounds well. Distilled water also lacks minerals that are beneficial for health.
How to Choose the Best Water Treatment System
Now that you’re familiar with the different types of water treatment systems, you might be wondering: How do I know which system is the best for my needs? The best water treatment system for you will depend on several key factors:
1. Type of Contaminants in Your Water
The first step in choosing the best water treatment system is to test your water. A water test will identify contaminants such as chlorine, heavy metals, microorganisms, and other impurities.
- For microbial contamination: UV purifiers or reverse osmosis systems are effective.
- For chemical contamination: Activated carbon filters are good for chlorine, pesticides, and VOCs, while distillation systems handle a broader range of chemicals.
- For hard water: A water softener will be most effective.
2. Water Source and Volume
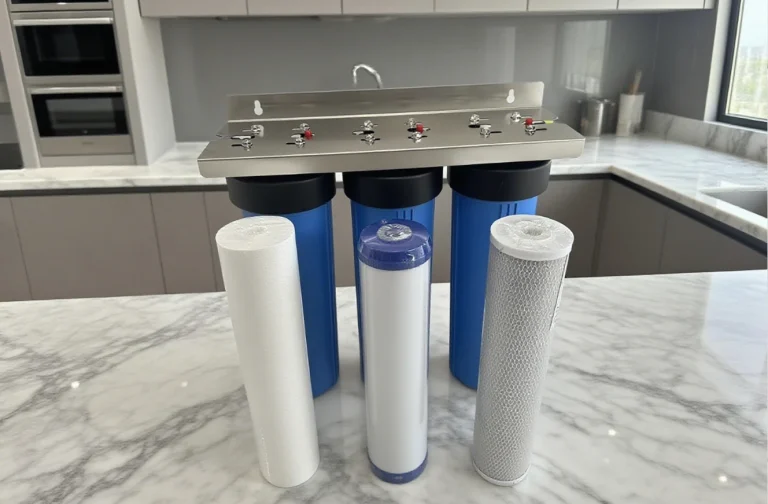
The volume of water you need to treat plays a role in determining which system is best. Larger households or businesses may need more robust filtration systems, such as whole-house reverse osmosis systems or a combination of filtration methods.
- For small households: Point-of-use systems, such as countertop or under-sink RO systems, may be sufficient.
- For larger homes or businesses: Whole-house filtration systems that combine several methods (e.g., activated carbon, water softeners, and RO) may be needed.
3. Maintenance Requirements
Different systems have varying levels of maintenance. Reverse osmosis systems, for example, require regular membrane replacement, while UV purifiers need occasional bulb replacements.
- Low maintenance: Activated carbon filters and UV systems are relatively low maintenance, requiring only periodic replacements.
- Higher maintenance: Reverse osmosis and distillation systems demand more frequent upkeep, including filter and membrane changes.
4. Budget Considerations
Water treatment systems come in a wide range of prices. While RO systems and distillers may be more expensive initially, they offer high performance in terms of contaminant removal. Activated carbon filters are more affordable but may not be sufficient on their own for some needs.
- Initial cost: RO systems and distillation units have higher upfront costs.
- Operating cost: Water softeners and carbon filters tend to have lower ongoing costs.
Case Study: Choosing the Best Water Treatment System for a Family Home
To help you understand how to choose the best water treatment system, let’s look at an example. A family living in a suburban area has well water that contains high levels of iron and sulfur, as well as occasional microbial contamination. They are concerned about both the taste of their water and the potential health risks.
Problem:
The water smells like rotten eggs due to sulfur, and they’ve noticed staining from iron buildup. Additionally, they are concerned about potential bacteria present in the well water.
Solution:
After conducting a water test, the family decided to install a whole-house water treatment system. This system included:
- A water softener to remove the iron.
- An activated carbon filter to remove sulfur and improve taste.
- A UV purifier to disinfect the water and kill any harmful bacteria.
Outcome:
The family reported an improvement in both taste and odor, and the water became clear without staining. They also had peace of mind knowing that the water was safe to drink.