BasideWT- Whole Home Water Filtration System & Replacement
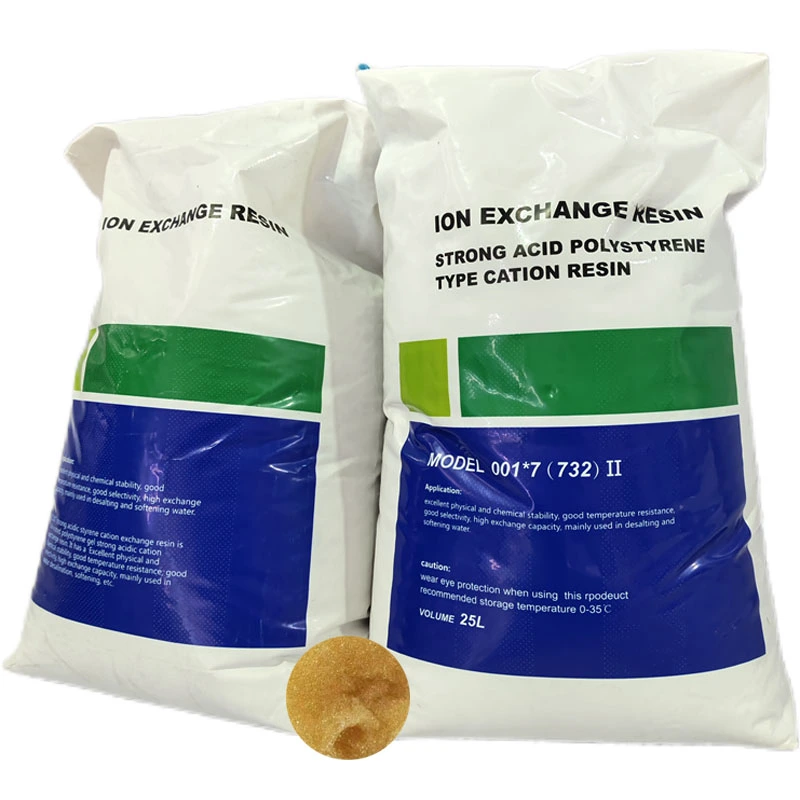
Mixed Bed Ion Exchange Water Softener Resin for Water Treatment 001×7 Strongly Acidic Cation Mixed Bed Exchange Resin
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
- Product Name: Water Softener Resin
- Alias: Cation Ion exchange Water Soften Resin
- Specifications: Water Soften Resin 001*7
- Appearance: Golden spherical particles
- Polymer structure: Styrene-DVB
- Style: Gel strong acid
- Application: Water softening
- Packing: Standard Exportation Package
Introduction to Water Softener Resin
Hard water causes scaling, reduces soap efficiency, and damages appliances. Water softener resin solves this by exchanging calcium/magnesium ions for sodium or hydrogen ions. Among various types, 001×7 strongly acidic cation mixed bed exchange resin stands out for high efficiency.
007 Ion Exchange Resin – Premium Strong Acid Cation Exchange Resin
1. Product Overview
The 007 ion exchange resin is a gel-type strong acid cation exchanger with superior stability, widely used in water treatment and industrial purification processes. Its sulfonated polystyrene-DVB matrix ensures high efficiency in ion removal applications.
2. Technical Specifications
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Strong acid cation exchange resin |
| Matrix | Styrene-divinylbenzene (DVB) copolymer |
| Functional Group | Sulfonic acid (-SO₃H) |
| Forms Available | Sodium (Na⁺) form for softening / Hydrogen (H⁺) form for demineralization |
| Appearance | Uniform amber-colored spherical beads (0.3-1.2 mm diameter) |
3. Key Features & Benefits
✔ High Exchange Capacity – Efficient removal of Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, and other cations,Fast Kinetics – Rapid ion exchange rates for continuous processes,Thermal/Chemical Stability – Withstands temperatures up to 120°C and pH 0-14,Food-Grade Options – Compliant with FDA/EC standards for beverage production
4. Primary Applications
- Water Softening – Replaces hardness ions (Ca²⁺/Mg²⁺) with Na⁺
- Demineralization – Produces high-purity water by removing all dissolved ions
- Industrial Processes – Sugar refining, pharmaceutical purification, metal recovery (e.g., nickel, cobalt)
5. Performance Data
- Operating Capacity: 1.8-2.2 eq/L (Na⁺ form)
- Max Operating Temp: 120°C (248°F)
- pH Range: 0-14
Note: For optimal performance, regenerate with 10% NaCl solution (softening) or HCl/NaOH (demineralization).
Step-by-Step Guide: Using 001×7 Resin Effectively
1. Pre-Treatment Inspection
Check water hardness (test strips help). If >250 ppm, water softener resin is essential.
2. Loading the Resin Tank
Fill ⅔ of the tank with 001×7 resin to allow proper flow.
3. Backwashing (First Use)
Run water backward for 10 mins to remove fines.
4. Regeneration Cycle
- Use NaCl (for softening) or HCl/NaOH (for mixed beds).
- Rinse thoroughly post-regeneration.
5. Performance Testing
Verify output hardness (<17 ppm = success).
Pro Tip: Our 2025 case study showed 30% longer resin life with monthly backwashing.

Common Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
❌ Using chlorinated water → Resin oxidation.
✅ Solution: Install a carbon pre-filter.
❌ Overloading the resin bed → Reduced efficiency.
✅ Solution: Follow manufacturer’s capacity guidelines.
❌ Skipping regeneration → Resin exhaustion.
✅ Solution: Set automatic regeneration cycles.
FAQs
Choosing the perfect water treatment system depends on your specific water quality, household size, and needs. We make it easy with our 3-step process:
Water quality testing – analyze your water for contaminants, hardness, and other factors.
Personalized Consultation – Our experts recommend systems based on your results, budget, and water usage.
Customized Solution – From whole-house filtration to targeted solutions (e.g., RO for drinking water, softeners for hard water), we tailor the system to your home.
To determine your water flow rate in gallons per minute (GPM), follow these simple steps:
Prepare for Testing:
- Prepare for Testing:
- Ensure all water fixtures in your home are turned off
- Select the faucet closest to your main water supply line (usually the kitchen sink or an outdoor spigot)
- Conduct the Test:
- Fully open the selected faucet
- Time how many seconds it takes to fill a 1-gallon container
- Repeat the test 2-3 times for accuracy
- Calculate Your Flow Rate:
Use this formula: Flow Rate (GPM) = 60 ÷ Fill Time (seconds)Example Calculation:- If your 1-gallon container fills in 15 seconds
- 60 ÷ 15 = 4 GPM
For more precise measurements or whole-home flow rate analysis, contact our water system specialists. We can help you determine if your current flow rate meets the requirements for any water treatment systems you’re considering.

1. Check Multiple Fixtures
Test water pressure at different faucets, showers, and appliances (e.g., kitchen sink, bathroom sink, outdoor hose).
If only one fixture has low pressure, the problem is likely localized (clogged aerator, faulty valve, or pipe issue).
If all fixtures have low pressure, the issue is systemic (main supply, pressure regulator, or water heater).
2. Inspect the Aerator or Showerhead
Unscrew the faucet aerator or showerhead and check for mineral deposits, debris, or rust.
Soak it in vinegar overnight to dissolve buildup, then rinse and reattach.
3. Check the Main Shutoff Valve
Locate the main water shutoff valve (usually near the water meter or where the main line enters the house).
Ensure it’s fully open (turn clockwise to close, counterclockwise to open).
1. Activated Carbon Filters
- Removes:
✅ Chlorine & chloramines
✅ Bad tastes & odors (e.g., sulfur)
✅ Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
✅ Some pesticides & herbicides
❌ Does not remove heavy metals, dissolved minerals, or microbes
2. Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems
- Removes:
✅ Heavy metals (lead, arsenic, mercury, cadmium)
✅ Dissolved salts (fluoride, nitrates, sulfates)
✅ Microplastics & sediment
✅ Bacteria & viruses (if combined with UV)
✅ Chlorine & chemicals (with carbon pre-filter)
❌ May remove beneficial minerals (can be remineralized)
3. Water Softeners (Ion Exchange)
- Targets:
✅ Calcium & magnesium (hardness)
✅ Low levels of iron & manganese
❌ Does not remove bacteria, chlorine, or heavy metals
4. UV Purifiers
- Kills:
✅ Bacteria (E. coli, coliform)
✅ Viruses (rotavirus, hepatitis)
✅ Protozoa (Giardia, Cryptosporidium)
❌ Does not remove chemicals, metals, or sediment
5. Sediment Filters
- Removes:
✅ Sand, rust, dirt
✅ Large particles & silt
❌ Does not remove dissolved contaminants
6. Whole-House Filtration Systems
Combines multiple methods (carbon + sediment + UV) for broad protection.
- UV: Kills bacteria/viruses but doesn’t remove chemicals or particles.
- RO (Reverse Osmosis): Removes 95–99% of contaminants (heavy metals, dissolved salts) but requires electricity.
- Activated Carbon: Absorbs chlorine, odors, and organic compounds—ideal for pre-filtration.










