BasideWT- Whole Home Water Filtration System & Replacement
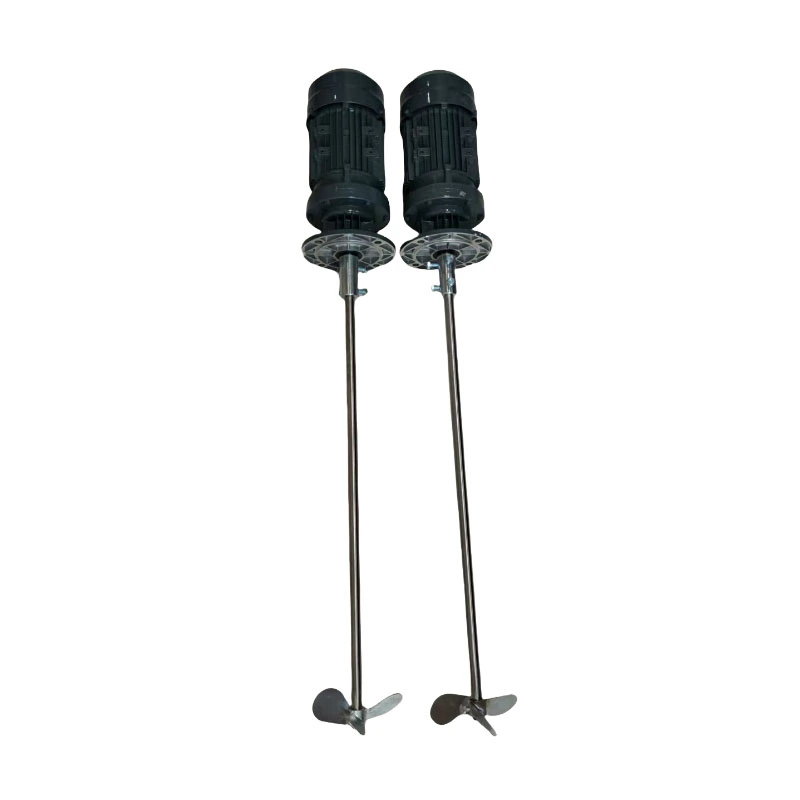
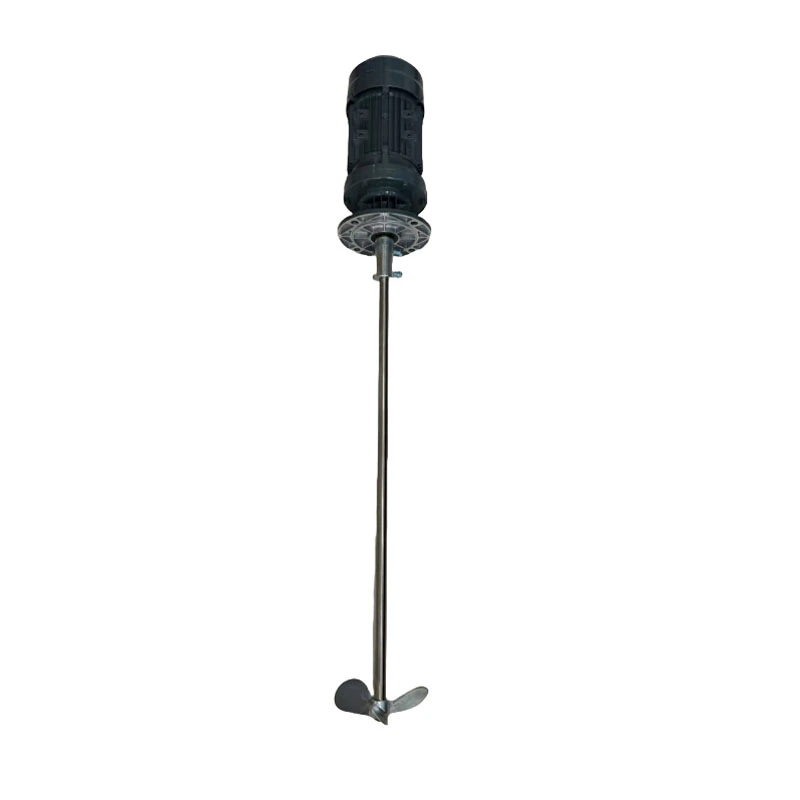
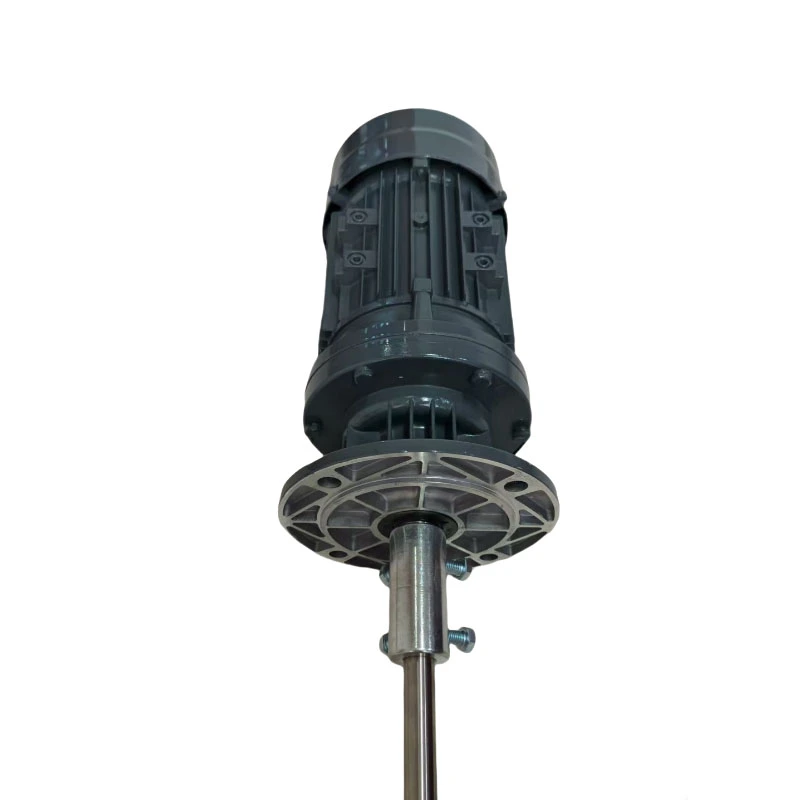
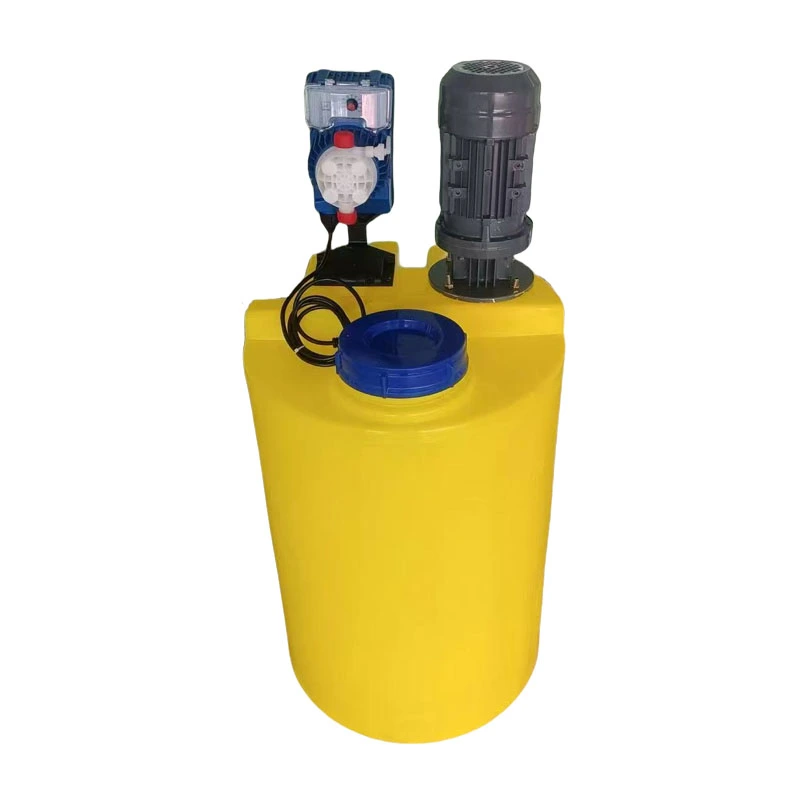
Chemical Dosing Pump and Electric Mixer Agitator for Mixing in Sewage Water
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
- Product Name: Electric Mixer Agitator
- Model: Agitator/Mixer
- Product Core: Pure Copper Core
- Features: Copper core coil, sturdy casing
- Shaft material: 304 stainless steel
- Mixer Type: Agitator
- Power: 0.37KW, 0.55KW, 0.75KW, 1.1KW, 1.5KW, 2.2KW,3KW
- Application: liquid and powder mixing
- Installation method: Vertical
- Working: High Speed Mixer
- Packing: Standard Exportation Package
Have you ever wondered what ensures chemicals blend perfectly in a vast sewage tank? The answer is a robust Electric Mixer Agitator. This powerhouse is the heart of effective wastewater treatment mixing. It transforms clumpy, inconsistent sewage into a homogeneous mixture. Therefore, processes like disinfection and neutralization work far better.
How Does a Sewage Water Mixer Agitator Function?
An industrial agitator mixer operates on a simple but vital principle. It uses a powerful electric motor to rotate an impeller submerged in the tank. This rotation creates controlled fluid dynamics. Essentially, it forces water and solids to move violently.
This action has one primary goal: achieve perfect uniformity. The wastewater agitator prevents solids from settling at the bottom. It also stops grease from floating on top. Instead, it creates a consistent, well-mixed slurry. This ensures every particle interacts equally with treatment chemicals.
Critical Applications for Wastewater Mixing Equipment
Where exactly is this technology deployed? Its uses are vast and varied across the treatment process.
- Chemical Blending: Mixing chemicals in water is a primary task. The agitator ensures coagulants, flocculants, and disinfectants disperse instantly. This eliminates weak spots and maximizes chemical efficiency.
- pH Neutralization Tanks: Here, the mixer blends acidic or alkaline waste with neutralizing agents. Consistent sewage water mixing is crucial. It maintains a stable pH level and prevents corrosive local pockets.
- Sludge Homogenization: In sludge storage tanks, solids constantly settle. An agitation system for sewage keeps this thick material in suspension. This makes pumping and further processing much easier and more consistent.
- Aerobic Digestion: Some processes require pumping air into sewage. A mixer agitator works alongside aerators. It spreads the oxygen bubbles evenly throughout the tank. This dramatically improves bacterial activity.
Parameters of Liquid Dosing Mixer

| Product Name | Liquid Dosing Mixer |
| Power | 0.37KW, 0.55KW, 0.75KW, 1.1KW, 1.5KW, 2.2KW,3KW |
| Voltage | 100V/110V/ 220V/ 240V/ 380V/ 415V |
| Material | SUS304 |
| Capabilities | Dispersing And Mixing |
| Core | Pure Copper Core |
| Installation method | Vertical |
| Model | Agitator/Mixer |
| Leaf type | three leaf; shape; three blade high efficiency type; custom made |
The Performance Characteristics of The Liquid Dosing Mixer
- Utilizes a planetary transmission principle with a cycloidal disc and pinwheel mechanism, ensuring precise and efficient power transmission through a small teeth difference design.
- High reduction ratio with outstanding transmission efficiency, achieving up to >90% efficiency in most applications.
- Compact and space-saving design with a high power-to-volume ratio, making it ideal for applications with limited installation space.
- Easy maintenance and repair due to its modular structure and simplified assembly, reducing downtime.
- Smooth and quiet operation with low vibration and minimal noise, suitable for noise-sensitive environments.
- Exceptional durability and long service life, thanks to robust manufacturing and high-quality materials that withstand rigorous operating conditions.
- High overload capacity and shock resistance, with low inertia for dynamic applications requiring frequent starts and stops.

FAQs
Choosing the perfect water treatment system depends on your specific water quality, household size, and needs. We make it easy with our 3-step process:
Water quality testing – analyze your water for contaminants, hardness, and other factors.
Personalized Consultation – Our experts recommend systems based on your results, budget, and water usage.
Customized Solution – From whole-house filtration to targeted solutions (e.g., RO for drinking water, softeners for hard water), we tailor the system to your home.
To determine your water flow rate in gallons per minute (GPM), follow these simple steps:
Prepare for Testing:
- Prepare for Testing:
- Ensure all water fixtures in your home are turned off
- Select the faucet closest to your main water supply line (usually the kitchen sink or an outdoor spigot)
- Conduct the Test:
- Fully open the selected faucet
- Time how many seconds it takes to fill a 1-gallon container
- Repeat the test 2-3 times for accuracy
- Calculate Your Flow Rate:
Use this formula: Flow Rate (GPM) = 60 ÷ Fill Time (seconds)Example Calculation:- If your 1-gallon container fills in 15 seconds
- 60 ÷ 15 = 4 GPM
For more precise measurements or whole-home flow rate analysis, contact our water system specialists. We can help you determine if your current flow rate meets the requirements for any water treatment systems you’re considering.

1. Check Multiple Fixtures
Test water pressure at different faucets, showers, and appliances (e.g., kitchen sink, bathroom sink, outdoor hose).
If only one fixture has low pressure, the problem is likely localized (clogged aerator, faulty valve, or pipe issue).
If all fixtures have low pressure, the issue is systemic (main supply, pressure regulator, or water heater).
2. Inspect the Aerator or Showerhead
Unscrew the faucet aerator or showerhead and check for mineral deposits, debris, or rust.
Soak it in vinegar overnight to dissolve buildup, then rinse and reattach.
3. Check the Main Shutoff Valve
Locate the main water shutoff valve (usually near the water meter or where the main line enters the house).
Ensure it’s fully open (turn clockwise to close, counterclockwise to open).
1. Activated Carbon Filters
- Removes:
✅ Chlorine & chloramines
✅ Bad tastes & odors (e.g., sulfur)
✅ Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
✅ Some pesticides & herbicides
❌ Does not remove heavy metals, dissolved minerals, or microbes
2. Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems
- Removes:
✅ Heavy metals (lead, arsenic, mercury, cadmium)
✅ Dissolved salts (fluoride, nitrates, sulfates)
✅ Microplastics & sediment
✅ Bacteria & viruses (if combined with UV)
✅ Chlorine & chemicals (with carbon pre-filter)
❌ May remove beneficial minerals (can be remineralized)
3. Water Softeners (Ion Exchange)
- Targets:
✅ Calcium & magnesium (hardness)
✅ Low levels of iron & manganese
❌ Does not remove bacteria, chlorine, or heavy metals
4. UV Purifiers
- Kills:
✅ Bacteria (E. coli, coliform)
✅ Viruses (rotavirus, hepatitis)
✅ Protozoa (Giardia, Cryptosporidium)
❌ Does not remove chemicals, metals, or sediment
5. Sediment Filters
- Removes:
✅ Sand, rust, dirt
✅ Large particles & silt
❌ Does not remove dissolved contaminants
6. Whole-House Filtration Systems
Combines multiple methods (carbon + sediment + UV) for broad protection.
- UV: Kills bacteria/viruses but doesn’t remove chemicals or particles.
- RO (Reverse Osmosis): Removes 95–99% of contaminants (heavy metals, dissolved salts) but requires electricity.
- Activated Carbon: Absorbs chlorine, odors, and organic compounds—ideal for pre-filtration.
REQUEST A QUOTE
RELATED PRODUCTS
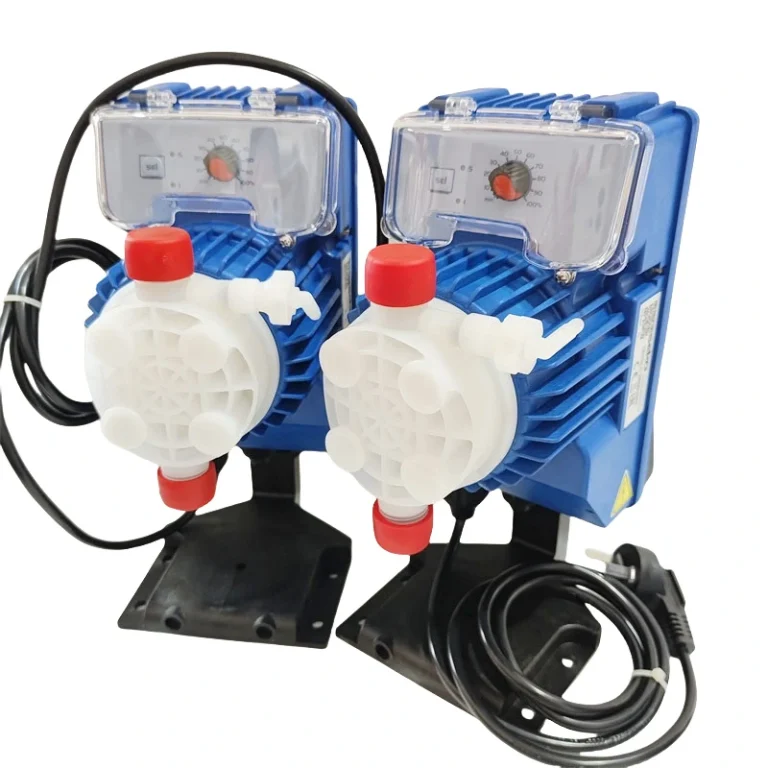

SEKO Tekna APG600/APG803 AKS603 – Automatic High-Efficiency Electromagnetic Diaphragm Metering Dosing Pump for Water Treatment Systems
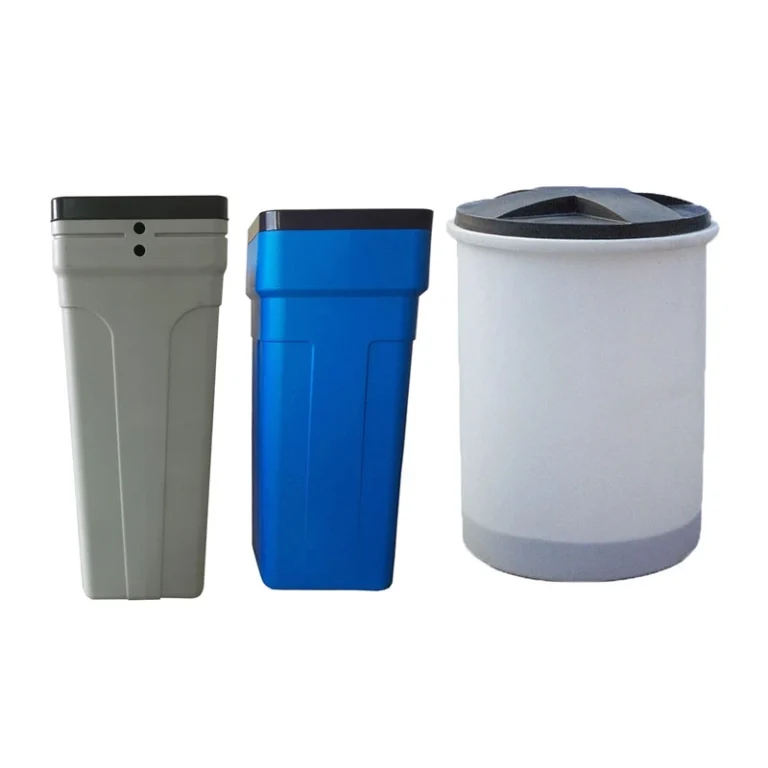

Rational Molding Round Water Softener Brine Tanks & Blow Molding Square Brine Tanks









