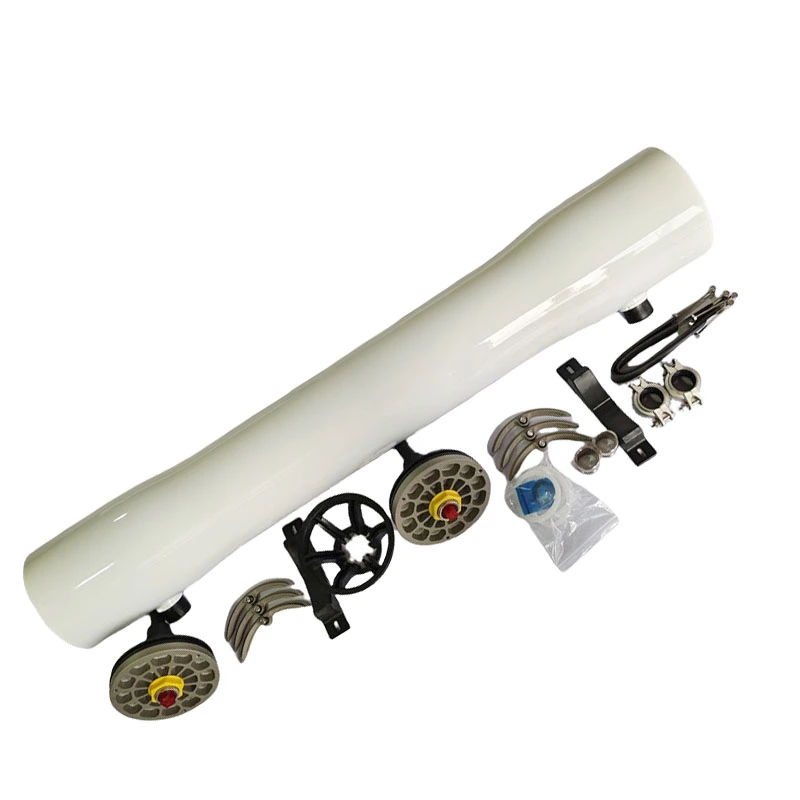
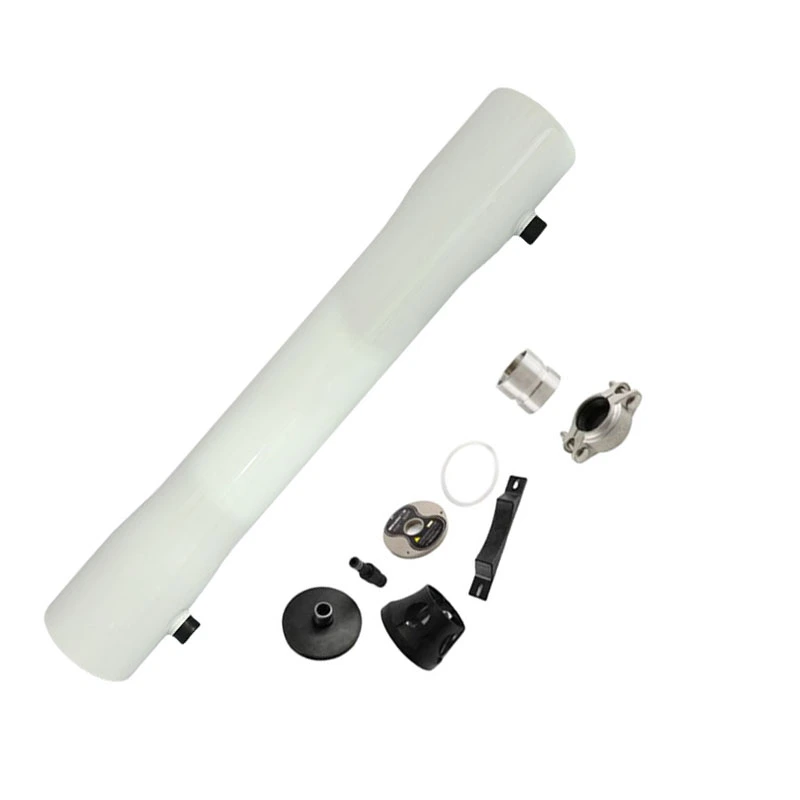
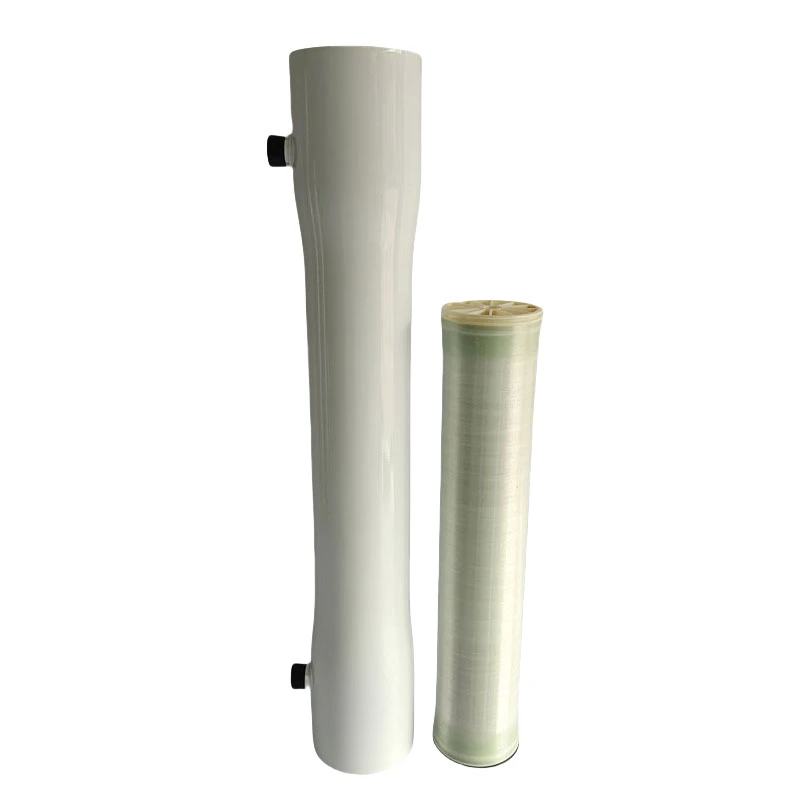
BasideWT- Whole Home Water Filtration System & Replacement
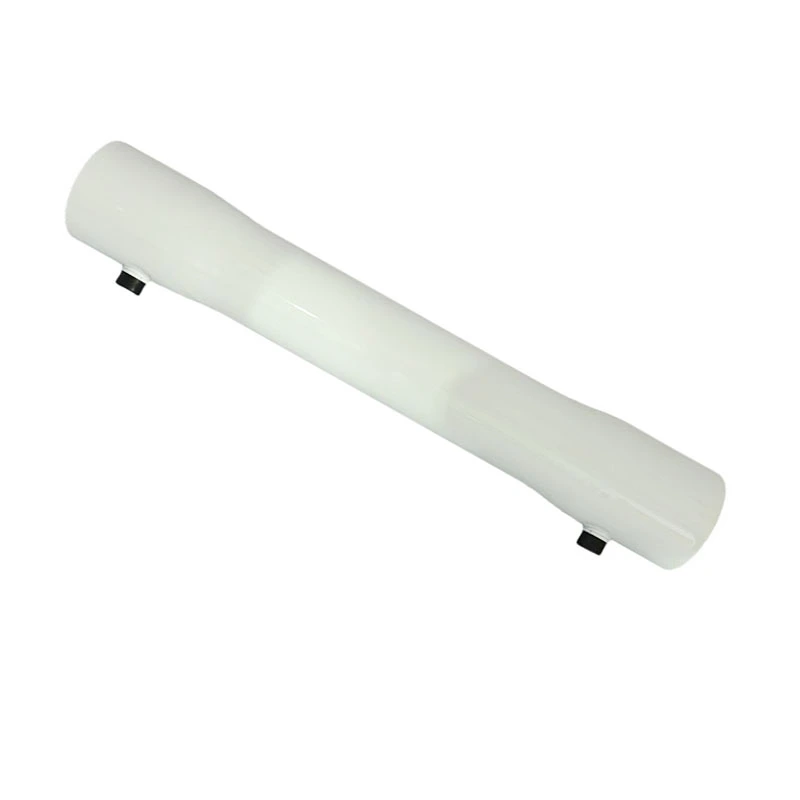
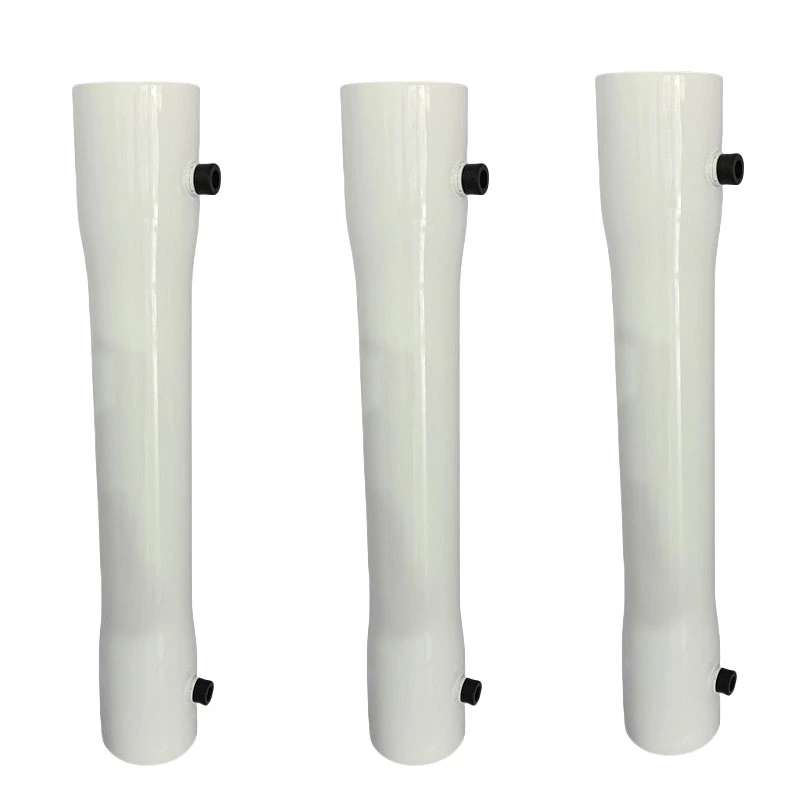
4040 8040 FRP RO Membrane Housing Fiberglass Pressure Vessels for Reverse Osmosis – Advanced Water Purification
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
- Product Name: Ro Membrane Housing
- Material: FRP
- Length: 1-4 Elements
- Type: Pure Water Treatment System
- Color: White
- Application: water treatment
- Size: 4" 8''
- Working Pressure: 300/450/600/800/1000 psi
- Processing Type: Reverse Osmosis
- Core Components: Pressure vessel
- Technology: RO Membrane Filtration
- Packing: Standard Exportation Package
Introduction: Why FRP RO Membrane Housing Matters
Reverse osmosis (RO) systems are vital for clean water, but their performance depends on durable FRP RO membrane housing. Fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) vessels offer unmatched strength and corrosion resistance compared to traditional materials.
In this guide, we’ll explore how FRP membrane housings enhance RO systems, compare them to alternatives, and provide actionable installation tips.
1. What is FRP RO Membrane Housing?
FRP RO membrane housing is a high-pressure vessel designed to hold RO membranes securely. Made from fiberglass-reinforced plastic, it withstands extreme pressures (up to 1,000 psi) and resists chemical degradation.
Key Benefits:
✔ Corrosion-proof (unlike steel housings),Lightweight yet durable (30% lighter than stainless steel),Long lifespan (15+ years with proper maintenance)
LSI Keywords: fiberglass pressure vessels, RO membrane housing, reverse osmosis housings
2. FRP vs. Stainless Steel: Which is Better?
Choosing the right material impacts system longevity. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | FRP Housing | Stainless Steel Housing |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (no rust) | Prone to chloride attacks |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy & bulky |
| Cost | Moderate | Expensive |
| Lifespan | 15+ years | 8-12 years |
⚠ Warning: Stainless steel fails in high-salinity environments, while FRP RO membrane housing performs consistently.
3. Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Proper setup ensures optimal performance. Follow these steps:
Inspect the Housing
Check for cracks or defects before installation. Even minor flaws can cause leaks under pressure.
Secure Mounting
Use reinforced brackets to prevent vibrations, which can damage membranes over time.
Connect Piping
Ensure all fittings are tight—loose connections lead to pressure drops (a common issue in 40% of RO failures^1^).
Pressure Testing
Run a 24-hour test at 1.5x operating pressure to confirm no leaks.
Membrane Insertion
Gently slide the RO membrane in, avoiding O-ring damage.
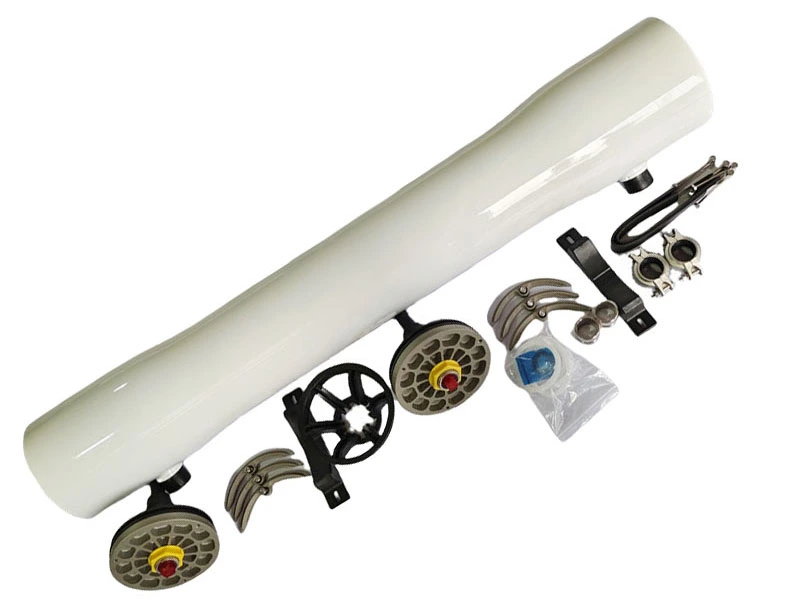

4. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many users unknowingly reduce their system’s efficiency.
❌ Using Low-Quality Seals
Cheap O-rings degrade fast, causing leaks. Always use manufacturer-approved parts.
❌ Ignoring Regular Cleaning
Calcium buildup reduces flow rates by up to 30%^2^. Flush membranes monthly.
❌ Over-Tightening Fittings
This cracks the housing. Hand-tighten, then use a wrench for just a quarter turn.
5. Real-World Case Study
In 2025, our team upgraded a seawater desalination plant from steel to FRP RO membrane housing. The result?
- 50% fewer maintenance calls
- 20% longer membrane life
- No corrosion issues after 18 months
This proves FRP’s superiority in harsh environments.
✅ Installation Checklist
- Inspect housing for defects
- Use reinforced mounting brackets
- Pressure-test before full operation
- Install high-quality O-rings
- Schedule regular cleaning
FAQs
Choosing the perfect water treatment system depends on your specific water quality, household size, and needs. We make it easy with our 3-step process:
Water quality testing – analyze your water for contaminants, hardness, and other factors.
Personalized Consultation – Our experts recommend systems based on your results, budget, and water usage.
Customized Solution – From whole-house filtration to targeted solutions (e.g., RO for drinking water, softeners for hard water), we tailor the system to your home.
To determine your water flow rate in gallons per minute (GPM), follow these simple steps:
Prepare for Testing:
- Prepare for Testing:
- Ensure all water fixtures in your home are turned off
- Select the faucet closest to your main water supply line (usually the kitchen sink or an outdoor spigot)
- Conduct the Test:
- Fully open the selected faucet
- Time how many seconds it takes to fill a 1-gallon container
- Repeat the test 2-3 times for accuracy
- Calculate Your Flow Rate:
Use this formula: Flow Rate (GPM) = 60 ÷ Fill Time (seconds)Example Calculation:- If your 1-gallon container fills in 15 seconds
- 60 ÷ 15 = 4 GPM
For more precise measurements or whole-home flow rate analysis, contact our water system specialists. We can help you determine if your current flow rate meets the requirements for any water treatment systems you’re considering.

1. Check Multiple Fixtures
Test water pressure at different faucets, showers, and appliances (e.g., kitchen sink, bathroom sink, outdoor hose).
If only one fixture has low pressure, the problem is likely localized (clogged aerator, faulty valve, or pipe issue).
If all fixtures have low pressure, the issue is systemic (main supply, pressure regulator, or water heater).
2. Inspect the Aerator or Showerhead
Unscrew the faucet aerator or showerhead and check for mineral deposits, debris, or rust.
Soak it in vinegar overnight to dissolve buildup, then rinse and reattach.
3. Check the Main Shutoff Valve
Locate the main water shutoff valve (usually near the water meter or where the main line enters the house).
Ensure it’s fully open (turn clockwise to close, counterclockwise to open).
1. Activated Carbon Filters
- Removes:
✅ Chlorine & chloramines
✅ Bad tastes & odors (e.g., sulfur)
✅ Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
✅ Some pesticides & herbicides
❌ Does not remove heavy metals, dissolved minerals, or microbes
2. Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems
- Removes:
✅ Heavy metals (lead, arsenic, mercury, cadmium)
✅ Dissolved salts (fluoride, nitrates, sulfates)
✅ Microplastics & sediment
✅ Bacteria & viruses (if combined with UV)
✅ Chlorine & chemicals (with carbon pre-filter)
❌ May remove beneficial minerals (can be remineralized)
3. Water Softeners (Ion Exchange)
- Targets:
✅ Calcium & magnesium (hardness)
✅ Low levels of iron & manganese
❌ Does not remove bacteria, chlorine, or heavy metals
4. UV Purifiers
- Kills:
✅ Bacteria (E. coli, coliform)
✅ Viruses (rotavirus, hepatitis)
✅ Protozoa (Giardia, Cryptosporidium)
❌ Does not remove chemicals, metals, or sediment
5. Sediment Filters
- Removes:
✅ Sand, rust, dirt
✅ Large particles & silt
❌ Does not remove dissolved contaminants
6. Whole-House Filtration Systems
Combines multiple methods (carbon + sediment + UV) for broad protection.
- UV: Kills bacteria/viruses but doesn’t remove chemicals or particles.
- RO (Reverse Osmosis): Removes 95–99% of contaminants (heavy metals, dissolved salts) but requires electricity.
- Activated Carbon: Absorbs chlorine, odors, and organic compounds—ideal for pre-filtration.
REQUEST A QUOTE
RELATED PRODUCTS
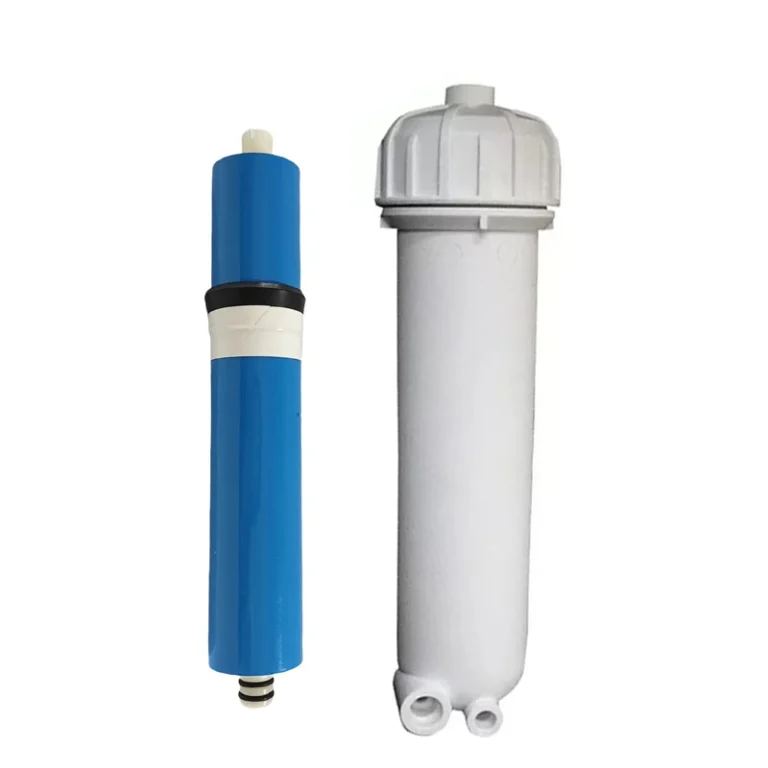

High Quality Double O Ring 1812/3012/3013/3213 Plastic RO Membrane Housing Shell for Residential RO Water Filter Use
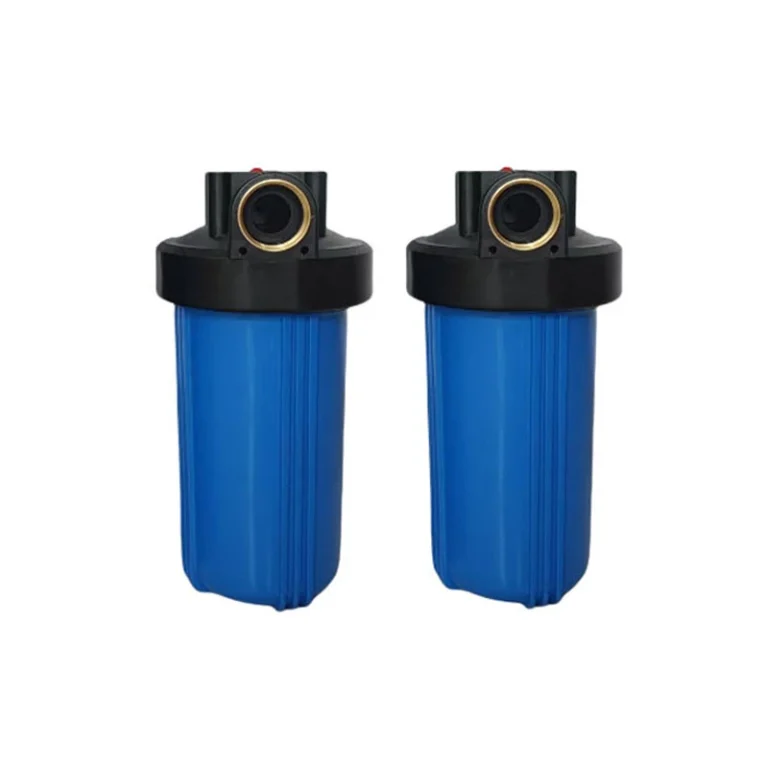

Whole House Sediment Water Filter Housing Blue Color – Fit for 4.5″ x 10″ Filters – NPT Brass Port 1″ 1.5” Inlet/Outlet (BB-10B)
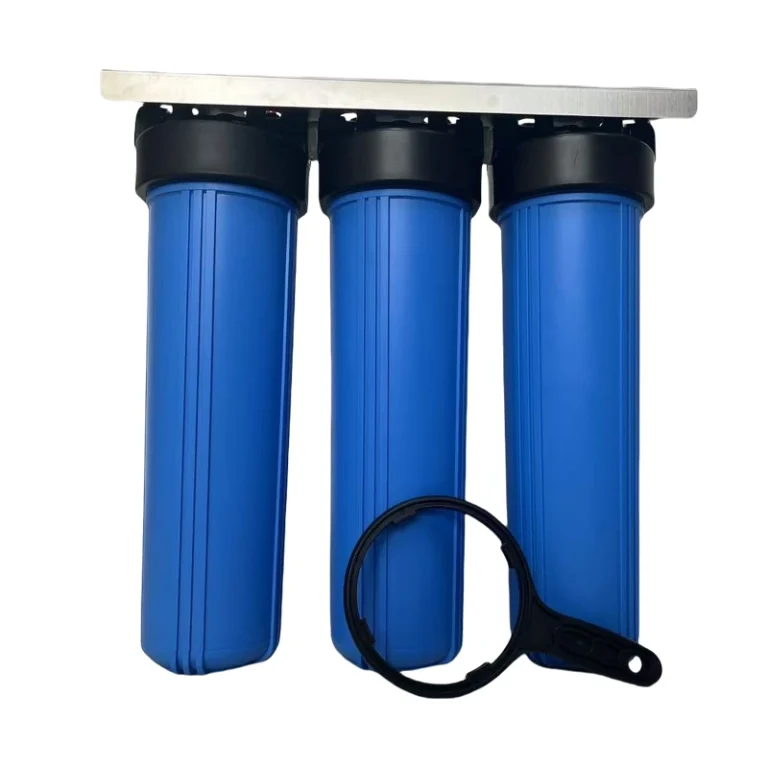

3 Stage Whole House Water Filter System 20″x4.5″ KDF Carbon Heavy Metal Filtration System

Industrial Bag Filter Housings | Precision Filters Supplier – Basidewt

10-inch Transparent Backflushing Water Purifier Livestock Waterline Filter Housing High Pressure Washer Filter with Sewage Outlet












