BasideWT- Whole Home Water Filtration System & Replacement
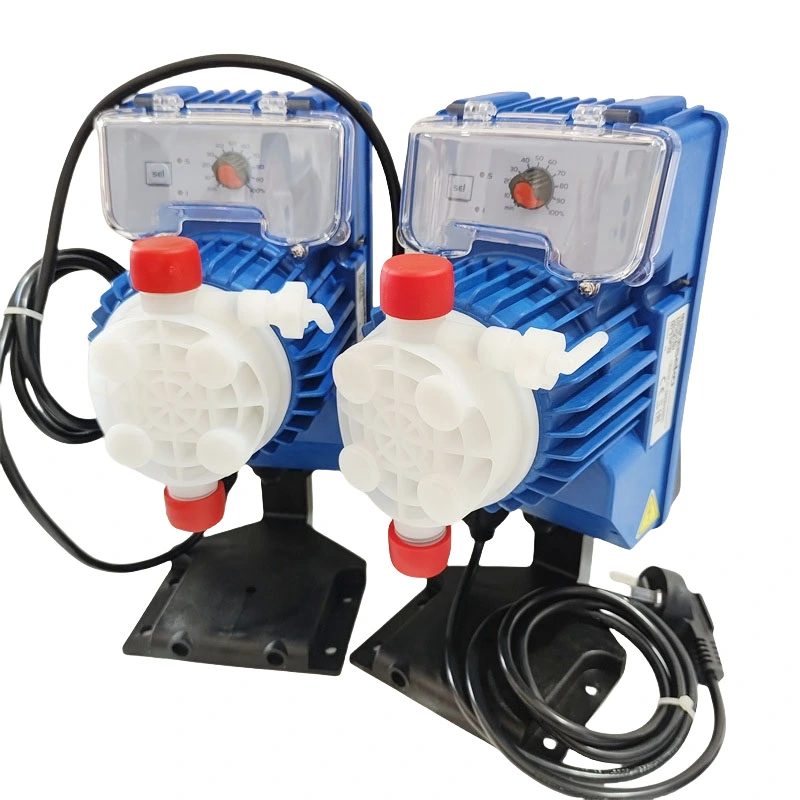
SEKO Tekna APG600/APG803 AKS603 – Automatic High-Efficiency Electromagnetic Diaphragm Metering Dosing Pump for Water Treatment Systems
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
- Product Name: Chemical Metering Pump
- Power Supply: 100-240 Vac50/60 Hz
- Flow rates: From 0.4 to 54 l/h
- Max back pressure: up to 20 bar
- Diaphragm Material: PTFE
- Pump head: PVDF
- Structure: Diaphragm Pump
- Power: Electric
- Application: Metering
- Use: Accurate control and delivery of liquid chemical agents
- Stroke rate: From 120 to 300 strokes/minute
- Packing: Standard Exportation Package
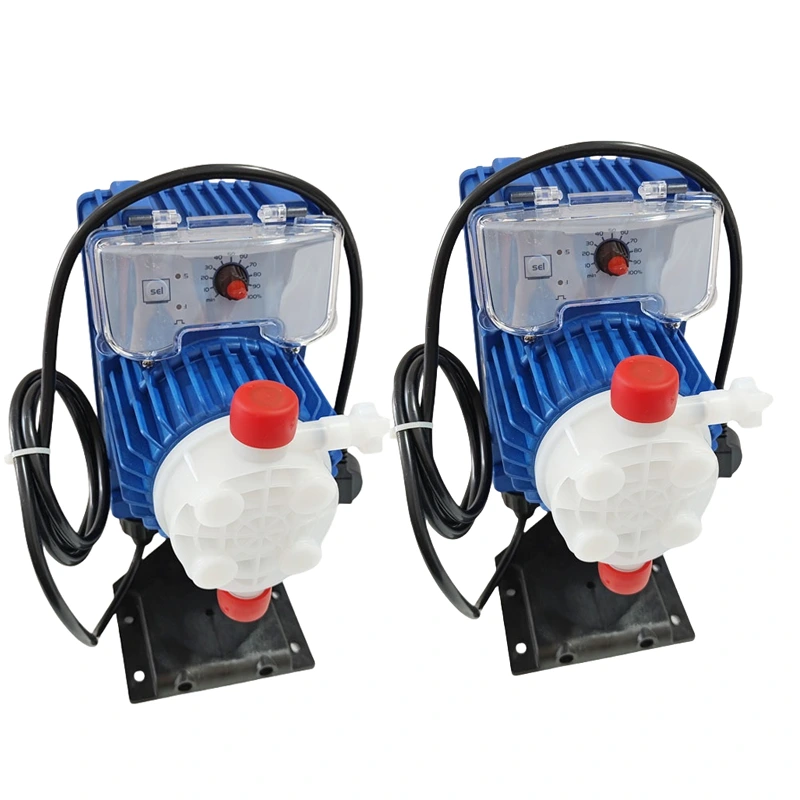
Seko Tekna EVO AKS Series – Analog Dosing Pump
The Seko Tekna EVO AKS Series is a constant-flow analog dosing pump with a manually adjustable flow rate via a front-panel knob. It offers two frequency ranges:
- 0–20% of max flow rate
- 0–100% of max flow rate
With just five sizes, the series covers a wide performance range:
- Flow rate: 0.4 to 54 L/h
- Back pressure: 0.1 to 20 bar
Power Supply Options
- 100–240 V ac, 50/60 Hz (universal input)
- Model 812 also supports 12 V dc
Materials & Compatibility
- Standard pump head: PVDF (high chemical resistance)
- Optional: PVC head (upon request)
Features & Accessories
- Manual priming for easy startup
- Standard installation kit includes:
- PVDF foot filter & injection valve
- PVC suction tube
- PE delivery tube
- PVC installation kit available (upon request)
Why Metering Dosing Pumps Are Critical in Water Treatment?
Water treatment plants rely on precise chemical dosing to maintain efficiency. A metering dosing pump, like the SEKO Tekna APG600/APG803 AKS603, ensures accuracy, reducing waste and operational costs.
Interesting fact: The global water treatment chemicals market will reach $72.5 billion by 2030 (Grand View Research, 2023). Without proper dosing, plants risk over-treatment (costly) or under-treatment (non-compliant).
How Does an Electromagnetic Diaphragm Pump Work?
Unlike peristaltic pumps, electromagnetic diaphragm metering pumps use a solenoid-driven mechanism for pulse-free, consistent flow. The SEKO Tekna series offers:
✔ Automatic adjustment (0-100% flow),High chemical resistance (PVDF/PVC options),Low energy consumption (up to 30% less than traditional pumps)
LSI Keywords: chemical dosing pump, precision dosing, water treatment pump, automated metering, diaphragm pump technology
SEKO Tekna Metering Dosing Pumps Technical Specifications
| Pump Model | Pressure (bar) | Flow Rate (L/h) | Frequency Max (stroke/min) | Stroke Capacity (cc/stroke) | Connection (mm) Suction | Connection (mm)Discharge | Power supply | Consumption [W] Min* | Consumption [W] Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKS 600 N | 20 | 2.5 | 120 | 0.35 | 4/6 | 4/7 | 100-240 V ac | 8 | 15 |
| 18 | 3 | 0.42 | |||||||
| 14 | 4.2 | 0.58 | |||||||
| 8 | 7 | 0.97 | |||||||
| AKS 603 N | 12 | 4 | 160 | 0.42 | 4/6 | 4/6 | 100-240 V ac | 15 | 18 |
| 10 | 5 | 0.52 | |||||||
| 8 | 6 | 0.63 | |||||||
| 2 | 8 | 0.83 | |||||||
| AKS 812 L | 10 | 3 | 200 | 0.25 | 4/6 | 4/6 | 12 V dc | 6.5 | 6.5 |
| 8 | 4 | 0.33 | |||||||
| 5 | 5 | 0.42 | |||||||
| AKL 800 N | 16 | 7 | 300 | 0.39 | 4/6 | 4/6 | 100-240 V ac | 15 | 26 |
| 10 | 10 | 0.56 | |||||||
| 5 | 15 | 0.83 | |||||||
| 1 | 18 | 1.00 | |||||||
| AKL 803 N | 5 | 20 | 300 | 1.11 | 8/12 | 8/12 | 100-240 V ac | 15 | 25 |
| 4 | 25 | 1.39 | |||||||
| 2 | 38 | 2.11 | |||||||
| 0.1 | 54 | 3.00 |
Step-by-Step Installation Guide for SEKO Tekna Metering Pumps
these 5 key steps for optimal performance:
- Check Power Compatibility (AC/DC, voltage range)
- Prime the Pump Manually (avoid dry runs!)
- Calibrate Flow Rate (use the front-panel knob)
- Install Foot Valve & Injection Kit (prevents backflow)
- Run a 30-Min Test Cycle (monitor for leaks/pulsation)
Pro Tip: We once saw a client skip calibration—their chlorine dosing was 20% off-spec within a week.
Common Mistakes When Using Metering Dosing Pumps
⚠ Avoid These Pitfalls:
- Ignoring Viscosity Limits (thick fluids need peristaltic pumps)
- Wrong Material Selection (e.g., PVC with strong acids)
- No Regular Maintenance (diaphragms degrade over time)
Counterintuitively, a higher-priced pump can save money long-term by reducing chemical waste.

Future Trends in Metering Pump Technology
Smart IoT-enabled dosing pumps are rising. SEKO’s 2025 models may include:
- Real-time flow analytics
- Auto-adjustment via pH sensors
- Predictive maintenance alerts
LSI Keywords: smart dosing system, industrial chemical pump, automated water treatment
Checklist for Optimal Metering Dosing Pump Performance
✅ Verify chemical compatibility,Calibrate quarterly,Inspect diaphragms every 6 months,Log flow rate deviations,Train staff on emergency stops
FAQs
Choosing the perfect water treatment system depends on your specific water quality, household size, and needs. We make it easy with our 3-step process:
Water quality testing – analyze your water for contaminants, hardness, and other factors.
Personalized Consultation – Our experts recommend systems based on your results, budget, and water usage.
Customized Solution – From whole-house filtration to targeted solutions (e.g., RO for drinking water, softeners for hard water), we tailor the system to your home.
To determine your water flow rate in gallons per minute (GPM), follow these simple steps:
Prepare for Testing:
- Prepare for Testing:
- Ensure all water fixtures in your home are turned off
- Select the faucet closest to your main water supply line (usually the kitchen sink or an outdoor spigot)
- Conduct the Test:
- Fully open the selected faucet
- Time how many seconds it takes to fill a 1-gallon container
- Repeat the test 2-3 times for accuracy
- Calculate Your Flow Rate:
Use this formula: Flow Rate (GPM) = 60 ÷ Fill Time (seconds)Example Calculation:- If your 1-gallon container fills in 15 seconds
- 60 ÷ 15 = 4 GPM
For more precise measurements or whole-home flow rate analysis, contact our water system specialists. We can help you determine if your current flow rate meets the requirements for any water treatment systems you’re considering.

1. Check Multiple Fixtures
Test water pressure at different faucets, showers, and appliances (e.g., kitchen sink, bathroom sink, outdoor hose).
If only one fixture has low pressure, the problem is likely localized (clogged aerator, faulty valve, or pipe issue).
If all fixtures have low pressure, the issue is systemic (main supply, pressure regulator, or water heater).
2. Inspect the Aerator or Showerhead
Unscrew the faucet aerator or showerhead and check for mineral deposits, debris, or rust.
Soak it in vinegar overnight to dissolve buildup, then rinse and reattach.
3. Check the Main Shutoff Valve
Locate the main water shutoff valve (usually near the water meter or where the main line enters the house).
Ensure it’s fully open (turn clockwise to close, counterclockwise to open).
1. Activated Carbon Filters
- Removes:
✅ Chlorine & chloramines
✅ Bad tastes & odors (e.g., sulfur)
✅ Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
✅ Some pesticides & herbicides
❌ Does not remove heavy metals, dissolved minerals, or microbes
2. Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems
- Removes:
✅ Heavy metals (lead, arsenic, mercury, cadmium)
✅ Dissolved salts (fluoride, nitrates, sulfates)
✅ Microplastics & sediment
✅ Bacteria & viruses (if combined with UV)
✅ Chlorine & chemicals (with carbon pre-filter)
❌ May remove beneficial minerals (can be remineralized)
3. Water Softeners (Ion Exchange)
- Targets:
✅ Calcium & magnesium (hardness)
✅ Low levels of iron & manganese
❌ Does not remove bacteria, chlorine, or heavy metals
4. UV Purifiers
- Kills:
✅ Bacteria (E. coli, coliform)
✅ Viruses (rotavirus, hepatitis)
✅ Protozoa (Giardia, Cryptosporidium)
❌ Does not remove chemicals, metals, or sediment
5. Sediment Filters
- Removes:
✅ Sand, rust, dirt
✅ Large particles & silt
❌ Does not remove dissolved contaminants
6. Whole-House Filtration Systems
Combines multiple methods (carbon + sediment + UV) for broad protection.
- UV: Kills bacteria/viruses but doesn’t remove chemicals or particles.
- RO (Reverse Osmosis): Removes 95–99% of contaminants (heavy metals, dissolved salts) but requires electricity.
- Activated Carbon: Absorbs chlorine, odors, and organic compounds—ideal for pre-filtration.













